

After the retention phase, participants took a deep breath and exhaled after 10 s.

Each round consisted of 30 deep breaths, after which participants exhaled and held their breath until the moment they felt the urge to breathe in.
WIM HOF METHOD BLOOD PRESSURE SERIES
The breathing exercises comprised a series of four rounds. The intervention consisted of 8 weeks of Wim Hof training and included three integrated parts: breathing exercises, cold exposure and meditation.

The instructor prepared a specific tailored program that followed the WHM procedure. Wim Hof psychophysiological training programĪpproximately 1 month before the expedition, the intervention group underwent introductory WHM training led by a certified instructor. We have followed the relevant EQUATOR STROBE guidelines for observational studies. The study was approved by the university hospital ethical committee (Medical Psychology and Psychopathology review board) of Charles University, First Faculty of Medicine approval no. Potential adverse effects were explained to participants. All participant details were de-identified and all participants provided signed informed consent related to this study. The expedition physician ascertained that none of the participants had any serious comorbidities, were taking any chronic medication that affected the central nervous system or the hormonal system (including hormonal contraception), had any mental health issues or chronic disorders (including hormonal or immune system) disorders, or had colored hair, and that all had American Society of Anesthesiology health scale scores of 1 to 2. Participants were divided into two groups based on their interest in the WMH psychophysiological training: an intervention group and a control group. Participants in this prospective observational study comprised all members of the expedition. Measures were taken at the start and at the end of an 8-week Antarctic expedition in a WMH training group and a control group. This research focused on psychometric measures related to long-term stress (Beck Depression Inventory and the Trauma Symptom Checklist-40 ) and neuroendocrine measures (cortisol, melatonin). 7, 8 All participants were healthy individuals who were researchers at the Antarctic station. Mendel Antarctic Station from January to March 2019. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of a WHM training program on psychological and neuroendocrine stress responses caused by extreme conditions during an expedition based at the J.G. In addition, this study reported that the WHM activated the left anterior and right middle insula, which are associated with self-reflection, and that respiration practice may affect sympathetic activation. 1, 2, 5, 6 A recent neuroimaging study using functional magnetic resonance imaging analyses showed that the WHM training program activates primary control centers for descending pain/cold stimuli modulation in the periaqueductal gray, possibly initiating a stress-induced analgesic response.
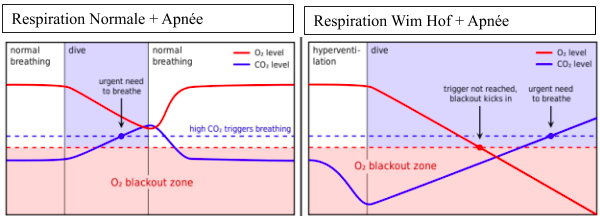
There are only a few studies on this novel training program and its psychophysiological effects, but findings suggest that the WMH has positive effects on immune and endocrine functions. The WHM consists of three main components: 1) breathing exercises, 2) various types of cold exposure, 1, 2 and meditation related to mindful body awareness, including enhancement of willpower and self-awareness. The WHM is based on cold exposure and special meditation techniques and was developed by a Dutch athlete named Wim Hof who exposed himself to extreme cold temperatures. Recent research provides preliminary evidence for the effectiveness of a novel psychophysiological training program called the Wim Hof Method (WHM).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
